L1 /
7
CH3041

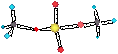
AEROSOL ADSORPTION

3) Aerosol
chemistry:
• Most aerosol
particles are composed of either
minerals (crust), sea-salt (sulphate) or organic matter (incl OC and BC aerosols).
Typical
disperse systems: d = 10nm
– 1mm.
Particles:
high surface area /mass 106 m2 g-1
Adsorption
Gases can adsorb on the large surface area. i(g) + aerosol D i(aer) i = adsorbing gas
Gases can adsorb on the large surface area. i(g) + aerosol D i(aer) i = adsorbing gas
A low
volatility gas will partition
between the
gas phase and the surface of the aerosol
according to: Kpart = [i(aer)] / ([ig][aerosol])
(Kpart = partition coefficient - m3/mg)
gas phase and the surface of the aerosol
according to: Kpart = [i(aer)] / ([ig][aerosol])
(Kpart = partition coefficient - m3/mg)