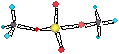
CH1012

L1 /
‹#›
L1 /
9
BROWNIAN MOTION.h

Brownian Motion
Viewed under low
magnification
colloidal particles change speed
and direction erratically in a characteristic way that is referred to as Brownian motion.
colloidal particles change speed
and direction erratically in a characteristic way that is referred to as Brownian motion.
• Collisions of the colloid
particles with the
dispersing medium causes this motion.
dispersing medium causes this motion.
• These collisions provide the
energy for
aggregation and collapse of the colloid.
A process called flocculation.
aggregation and collapse of the colloid.
A process called flocculation.
• A. Einstein explained Brownian motion
using a molecular model in 1905.
using a molecular model in 1905.
423oC
liquid Pb in solid Al !
Brown used pollen in H2O