L1 /
8
CH1012

BOLTZMAN
DISTRIBUTIONS

Boltzman
rationalized the distribution of energies
using the Boltzman equation:
using the Boltzman equation:
Where
Ni , Nj are the number of
molecules with energy Ei or
energy Ej, respectively.
kB = Boltzmans constant (1.38 x 10-23 J /K)
T = temperature
molecules with energy Ei or
energy Ej, respectively.
kB = Boltzmans constant (1.38 x 10-23 J /K)
T = temperature
Boltzmans
equation indicates that the
lowest energy states (j) are more
populated by molecules than the
higher energy states (i).
lowest energy states (j) are more
populated by molecules than the
higher energy states (i).
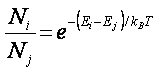

T1 T2
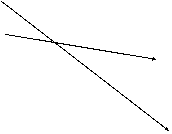
The
vibrational
energies of gas
molecules show the typical
exponential decline characteristic
of the Boltzman distribution.
At the higher temperature (T2) more
states are occupied.
molecules show the typical
exponential decline characteristic
of the Boltzman distribution.
At the higher temperature (T2) more
states are occupied.