L1 /
6
CH1012

KINETIC
MOLECULAR
THEORY OF GASES
THEORY OF GASES

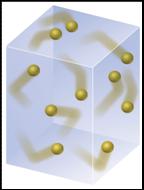
Kinetic Molecular
Model of Gases
A
quantitative model used to
describe the macroscopic
properties of an ideal gas.
describe the macroscopic
properties of an ideal gas.
Based
on three postulates:
1) Molecules of mass m are in
ceaseless straight line motion.
1) Molecules of mass m are in
ceaseless straight line motion.
2)
Size of particles is negligible.
3)
The molecules do not interact
or they collide perfectly elastically.
or they collide perfectly elastically.
vThe pressure
of a gas results from the number of collisions
per unit time on the container walls.
vEach gas molecule
has a different kinetic
energy as it travels with a
different translational (sliding) motion
ie. different velocity and direction (½mv2)